Chapter 2 - Epithelium
Epithelium forms continuous sheets of cells that line internal surfaces and cover the external surface of the body. It is a selective barrier that protects tissues and is often involved in absorption or secretion. A basement membrane separates an epithelium from the underlying connective tissue.
Epithelia are classified based on three criteria:
- Number of cell layers (simple or compound)
- Shape of surface cells (squamous, cuboidal or columnar)
- Specializations (cilia, keratin or goblet cells)
Epithelial cells are polarized:
- Apical surface - faces the lumen or the external environment
- Microvilli, cilia, stereocilia
- Lateral surface - faces the sides of adjacent cells
- Tight junctions (zonula occludens), adherens junction (zonula adherens), desmosomes (macula adherens), gap junctions
- Basal surface - attaches to the basement membrane
- Basement membrane, hemidesmosomes
An epithelium does not contain blood vessels and receives nourishment via diffusion from the underlying connective tissue.
Glands are formed by the down growth of an epithelium into the underlying connective tissue (discussed in Chapter 12 - Exocrine Glands).
It is not necessary to learn the names of specific tissues for this chapter, but rather learn to recognize variations in epithelia.
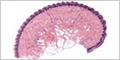
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium consists of a single layer of flattened cells. The thinness of these cells facilitates the transfer of materials (e.g., gases, fluids or nutrients) across the epithelium.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple cuboidal epithelium consists of a single layer of cuboidal cells. This epithelium is often associated with absorption, secretion, or excretion of waste matter.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium consists of a single layer of cells that are taller than they are wide. This epithelium is often associated with absorption or secretion.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified epithelium appears to be stratified because the nuclei of the epithelial cells are at different levels. However, every cell is in contact with the basement membrane, but not all cells reach the lumen.
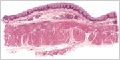
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium has multiple layers of cells becoming flattened as they move from the basal layer to the apical layers. It provides protection from abrasion and is keratinized on the external surface of the body.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified cuboidal epithelium has multiple layers of cells with an outermost layer of cuboidal cells. Limited distribution - found in the lining of larger ducts.
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional epithelium (urothelium) is adapted for extensibility and is restricted to the urinary tract. It has multiple layers of cells with an outermost layer of much larger, dome-shaped cells (umbrella cells) that change shape during contraction and distention.