Chapter 6 - Nerve Tissue
The nervous system, one of the four basic tissue types, is a complex network that coordinates actions and transmits signals between different parts of the body.
Anatomically, it can be divided into two main parts:
- Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord
- Nervous System (PNS) - nerves and clusters of cell bodies (ganglia) located outside the CNS
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a subdivision of the PNS that regulates involuntary physiological processes, such as glands, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. It can be divided into several branches:
- Sympathetic Nervous System - involved in functions requiring quick responses (i.e., fight-or-flight response), increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and blood flow to muscles
- Parasympathetic Nervous System - regulates functions that do not need a rapid response (i.e., the rest-and-digest system), decreases heart rate and blood pressure, and stimulates digestion.
- Enteric Nervous System - sometimes regarded as a third division that controls the gastrointestinal tract, operating relatively independently of the CNS, while still being influenced by the other two divisions
NEURON
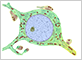
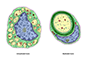
The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are highly polarized cells with a cell body containing the nucleus, a number of branching dendrites, and a single, long axon. The dendrites receive incoming signals, the cell body integrates them, and the axon transmits a signal to other neurons or cells.
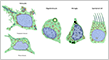
While most cells have similar shapes in other tissues, nerve cells exhibit a wide variety of shapes.
??? Types of Neurons (multipolar, bipolar, unipolar)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
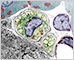
The human brain contains around 86 billion neurons organized in complex networks.
Neurons
Neurons vary considerably in shape and size, but most share a common structure.
Glial Cells
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells that support, nourish, and myelinate the neurons of the central nervous system (CNS). Glial cells and their extensive processes essentially replace the connective tissue found in other organ systems.
There are four main types of glial cells in the CNS:
- Protoplasmic Astrocytes - stellate cells with many highly branched processes
- Fibrous Astrocytes - cells with fewer long, less branched processes
- Oligodendrocytes - form myelin sheaths around some axons
- Microglia - mobile cells that resemble macrophages
- Ependymal Cells - ciliated, epithelial-like cells that line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord
??? Ultrastructure of glial cells
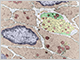
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
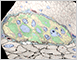
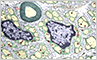
Peripheral nerve cell bodies are only present in peripheral ganglia, where they are surrounded by satellite cells. Peripheral nerves contain bundles of axons, which are supported by Schwann cells. Both are surrounded by connective tissue sheaths containing fibroblasts and a collagen-rich matrix.
There are two main types of glial cells in the PNS:
- Satellite Cells - small cuboidal cells that surround the cell bodies of nerve cells in ganglia
- Schwann Cells - isolates axons from the surrounding extracellular compartment
- Non-Myelinating - Schwann cells encapsulates multiple non-myelinated axons
- Myelinating - Schwann cells wrap a segment of a single axon with a myelin sheath
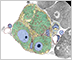
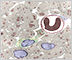
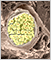
Ganglia
???
??? Myenteric ganglia are different
Peripheral Nerves
Peripheral nerves contain the axons of both motor neurons and sensory neurons that connect with the spinal cord. They are surrounded by multiple layers of connective tissue.
Schwann cells enclose groups of unmyelinated axons.
Myelinated axons are a portion of a neuron that is encapsulated by a fatty layer called the myelin sheath. The speed of conduction of myelinated axons is faster than unmyelinated axons.
Nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the myelin sheath that surrounds the axons of neurons.
??? Nodes of Ranvier
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction (or motor endplate) is a specialized synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell. It transmits a signal to the muscle fiber causing its contraction.